- Products ProductsLocation Services
Solve complex location problems from geofencing to custom routing
PlatformCloud environments for location-centric solution development, data exchange and visualization
Tracking & PositioningFast and accurate tracking and positioning of people and devices, indoors or outdoors
APIs & SDKsEasy to use, scaleable and flexible tools to get going quickly
Developer EcosystemsAccess Location Services on your favorite developer platform ecosystem
- Documentation DocumentationOverview OverviewServices ServicesApplications ApplicationsDevelopment Enablers Development EnablersContent ContentHERE Studio HERE StudioHERE Workspace HERE WorkspaceHERE Marketplace HERE MarketplacePlatform Foundation and Policy Documents Platform Foundation and Policy Documents
- Pricing
- Resources ResourcesTutorials TutorialsExamples ExamplesBlog & Release Announcements Blog & Release AnnouncementsChangelog ChangelogDeveloper Newsletter Developer NewsletterKnowledge Base Knowledge BaseFeature List Feature ListSupport Plans Support PlansSystem Status System StatusLocation Services Coverage Information Location Services Coverage InformationSample Map Data for Students Sample Map Data for Students
- Help
Correlate road attributes to segment geometry
Objectives: Understand how to correlate road attribute values to segment geometry by following the attribution referencing model of HERE Map Content.
Complexity: Intermediate
Time to complete: 45 min
Prerequisites: Verify credentials, Organize your work in projects
Source code: Download
This example demonstrates how to read road attribute values and correlate them to segment geometry following the attribution referencing model of HERE Map Content.
The application uses the Data Client Library to start with a single partition in the Road Attributes layer of HERE Map Content.
The Data Client Library then aggregates its corresponding segment geometry into paved and unpaved segments. The output is a single GeoJSON tile with the paved segments colored in green and the unpaved segments colored in red.
This single GeoJSON partition, which the application processes, is 17302687.
You can inspect this tile in the Road Attributes layer of HERE Map Content in the portal:
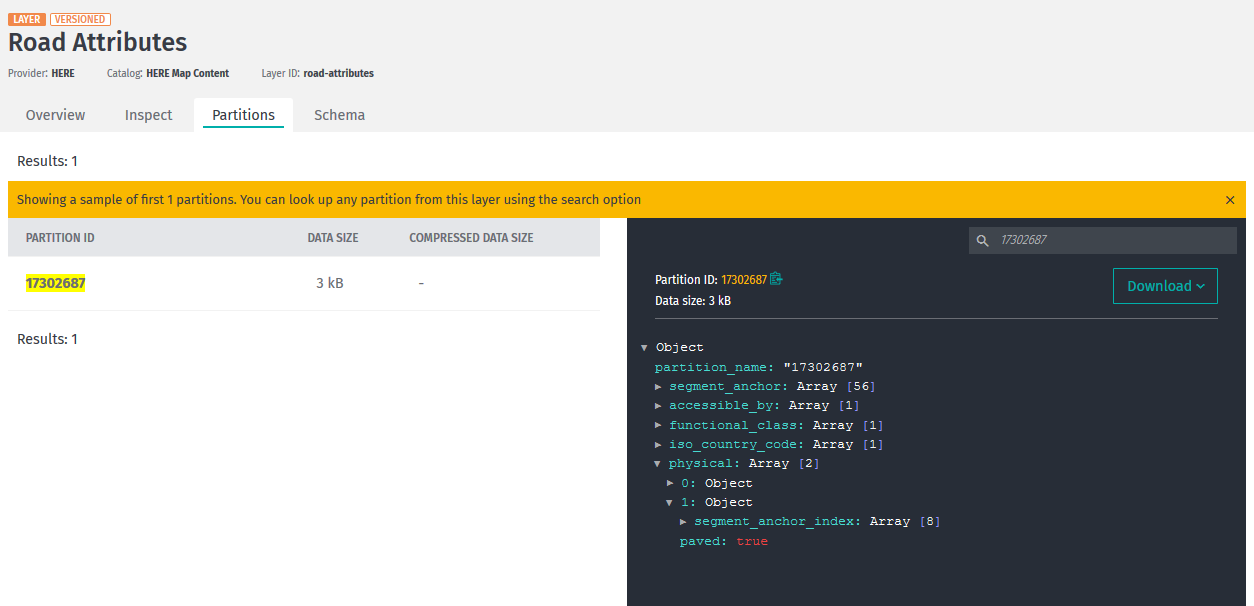
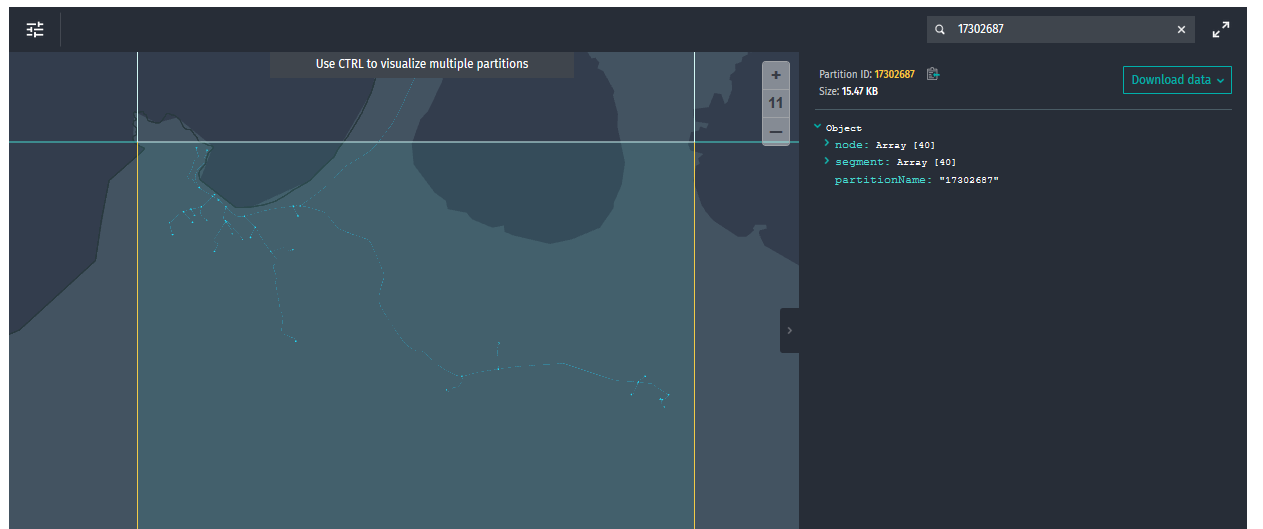
The geometry for the partition is in the Road Topology & Geometry layer.
Create the output catalog
The output catalog contains a single GeoJSON layer. The following code snippet shows the configuration file. Replace {{YOUR_CATALOG_ID}} with your own unique ID such as {{YOUR_USERNAME}}-road-attr-walkthru.
{
"id": "{{YOUR_CATALOG_ID}}",
"name": "Paved and unpaved road segments from Road Attribute Walkthrough",
"summary": "Paved and unpaved road segments from Road Attribute Walkthrough",
"description": "Paved and unpaved road segments from Road Attribute Walkthrough",
"layers": [
{
"id": "roadsegments",
"name": "roadsegments",
"summary": "Paved and unpaved road segments",
"description": "Paved and unpaved road segments",
"contentType": "application/vnd.geo+json",
"layerType": "versioned",
"digest": "sha-1",
"volume": {
"volumeType": "durable"
},
"partitioning": {
"scheme": "heretile",
"tileLevels": [12]
},
"coverage": {
"adminAreas": [
"NZ"
]
}
}
]
}
The OLP CLI requires a valid set of HERE credentials to authenticate itself with the Data Services, so verify that the Verify your credentials tutorial returns the expected result.
-
If you have not already done so, download and unzip the Java and Scala examples and the CLI.
-
Add the
tools/OLP_CLIfolder of the unzipped file to your${PATH}. -
Create the catalog with the following command:
olp catalog create {{YOUR_CATALOG_ID}} \
"Paved and unpaved road segments from Road Attribute Walkthrough" \
--config output-catalog.json \
--scope {{YOUR_PROJECT_HRN}}
The CLI returns as follows:
Catalog {{YOUR_CATALOG_HRN}} has been created.
Note
If a billing tag is required in your realm, update the config file by adding the billingTags: ["YOUR_BILLING_TAG"] property to the layer section.
Set up the Maven project
Create the following folder structure for the project:
road-attr-walkthru
└── src
└── main
├── java
└── scala
You can do this with a single bash command:
mkdir -p road-attr-walkthru/src/main/{java,scala}
The POM for this example is identical to that in the first Maven example, except for its dependencies, repositories, and build sections:
The dependencies are as follows:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.here.platform.data.client</groupId>
<artifactId>data-client_${scala.compat.version}</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.here.platform.data.client</groupId>
<artifactId>data-engine_${scala.compat.version}</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.here.platform.pipeline</groupId>
<artifactId>pipeline-interface_${scala.compat.version}</artifactId>
</dependency>
Scala
Java
<dependency>
<groupId>com.here.schema.rib</groupId>
<artifactId>road-attributes_v2_scala_${scala.compat.version}</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.here.schema.rib</groupId>
<artifactId>topology-geometry_v2_scala_${scala.compat.version}</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.json4s</groupId>
<artifactId>json4s-jackson_${scala.compat.version}</artifactId>
<version>3.5.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.here.schema.rib</groupId>
<artifactId>road-attributes_v2_java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.here.schema.rib</groupId>
<artifactId>topology-geometry_v2_java</artifactId>
</dependency>Since the application uses the Scala bindings from the HERE Map Content schema, you must add the following repositories section to resolve schema artifacts.
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>HERE_PLATFORM_ARTIFACT</id>
<layout>default</layout>
<url>here+https://artifact.api.platform.here.com/v1/artifact</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
You also need the following extensions section under build.
<extensions>
<extension>
<groupId>com.here.platform.artifact</groupId>
<artifactId>artifact-wagon</artifactId>
<version>${artifact.wagon.version}</version>
</extension>
</extensions>
For more information on the Artifact Service, which resolves schemas, see "Artifact Service" in the Dependency Management documentation.
Implement the application
The respective Scala and Java implementations are as follows:
Scala
Java
/*
* Copyright (c) 2018-2023 HERE Europe B.V.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
import akka.actor.CoordinatedShutdown.UnknownReason
import akka.actor.{ActorSystem, CoordinatedShutdown}
import com.here.hrn.HRN
import com.here.platform.data.client.engine.scaladsl.{DataEngine, WriteEngine}
import com.here.platform.data.client.model.VersionDependency
import com.here.platform.data.client.scaladsl.{DataClient, NewPartition, PublishApi, QueryApi}
import com.here.platform.pipeline.PipelineContext
import com.here.schema.geometry.v2.geometry.LineString
import com.here.schema.rib.v2.common.Reference
import com.here.schema.rib.v2.road_attributes_partition.RoadAttributesPartition
import com.here.schema.rib.v2.topology_geometry_partition.TopologyGeometryPartition
import com.typesafe.config.{Config, ConfigFactory, ConfigValueFactory}
import org.json4s.JsonDSL._
import org.json4s.jackson.JsonMethods._
import scala.concurrent._
import scala.concurrent.duration._
object RoadAttrWalkthruScala {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// Initialize the Akka Actor System used by the Data Client Library.
val config: Config = ConfigFactory
.empty()
.withValue("here.platform.data-client.endpoint-locator.discovery-service-env",
ConfigValueFactory.fromAnyRef("custom"))
.withValue(
"here.platform.data-client.endpoint-locator.discovery-service-url",
// Please use https://api-lookup.data.api.platform.hereolp.cn URL for China Environment
// We should define a custom URL, specific to China Environment, for a discovery service
// endpoint that allows discovering various Data Service APIs like publish, metadata, query, etc.
ConfigValueFactory.fromAnyRef("https://api-lookup.data.api.platform.here.com")
)
implicit lazy val actorSystem: ActorSystem =
ActorSystem.create("RoadAttrWalkthruScalaExampleApp", config)
try {
val pipelineContext = new PipelineContext()
val hereMapContentHrn = pipelineContext.config.inputCatalogs("hereMapContent")
val hereMapContentVersion = pipelineContext.job.get.inputCatalogs("hereMapContent").version
// Choosing a Chatham Islands partition in New Zealand to keep things simple.
// Please use partition 23551658 in Tibet for China Environment.
// Feel free to replace this with one or more other partitions of interest.
val roadAttrPartitionNames = Seq("17302687")
val outputHrn = pipelineContext.config.outputCatalog
// Initialize the I/O for the catalog.
val queryApi = DataClient().queryApi(hereMapContentHrn)
val readEngine = DataEngine().readEngine(hereMapContentHrn)
val writeEngine = DataEngine().writeEngine(outputHrn)
val publishApi = DataClient().publishApi(outputHrn)
val waitDuration = 60 seconds
// Retrieve the metadata for the road-attribute partition(s).
val roadAttrMetadata = Await.result(queryApi.getPartitionsById(hereMapContentVersion,
"road-attributes",
roadAttrPartitionNames),
waitDuration)
roadAttrMetadata.foreach { metadata =>
// For users using platform.here.com:
// https://here-tech.skawa.fun/documentation/data-client-library/dev_guide/client/get-data.html
// https://here-tech.skawa.fun/documentation/here-map-content/topics/road-layer.html
// For users using platform.hereolp.cn:
// https://here-tech.skawa.fun/cn/documentation/data-client-library/dev_guide/client/get-data.html
// https://repo.platform.hereolp.cn/artifactory/open-location-platform-docs/Data_Specifications/HERE_Map_Content/HERE_Map_Content_OLP_China_v2019-05_Data_Specification.pdf
// Retrieve the payload for the road-attribute partition and decode its contents.
val roadAttributesPartition =
Await.result(readEngine.get(metadata, RoadAttributesPartition.parseFrom), waitDuration)
// For users using platform.here.com:
// https://here-tech.skawa.fun/documentation/here-map-content/topics_api/com.here.schema.rib.v2.physicalattribute.html
// For users using platform.hereolp.cn:
// https://repo.platform.hereolp.cn/artifactory/open-location-platform-docs/Data_Specifications/HERE_Map_Content/HERE_Map_Content_OLP_China_v2019-05_Data_Specification.pdf
// Separate the physical attribute values combinations into those which have paved=true, and those which have paved=false.
val (paved, unpaved) = roadAttributesPartition.physical.partition(_.paved)
// For users using platform.here.com:
// https://here-tech.skawa.fun/documentation/here-map-content/topics/anchor.html
// For users using platform.hereolp.cn:
// https://repo.platform.hereolp.cn/artifactory/open-location-platform-docs/Data_Specifications/HERE_Map_Content/HERE_Map_Content_OLP_China_v2019-05_Data_Specification.pdf
// Get the segment anchor indices for the paved and unpaved segments.
val pavedSegmentAnchorIndices = paved.flatMap(_.segmentAnchorIndex)
val unpavedSegmentAnchorIndices = unpaved.flatMap(_.segmentAnchorIndex)
// Follow the segment anchor references to get the name of the partition(s)
// which contain the actual segment geometry within the topology-geometry layer.
val pavedTopologyPartitions =
getTopologyPartitionNames(pavedSegmentAnchorIndices, roadAttributesPartition)
val unpavedTopologyPartitions =
getTopologyPartitionNames(unpavedSegmentAnchorIndices, roadAttributesPartition)
// Retrieve the metadata for the referenced topology-geometry partitions.
val topoMetadata = Await.result(
queryApi.getPartitionsById(hereMapContentVersion,
"topology-geometry",
(pavedTopologyPartitions ++ unpavedTopologyPartitions).toSeq),
waitDuration)
// Retrieve the payloads and decode the content of the referenced topology-geometry partitions.
// We need to do this because it is not guaranteed that every segment anchor refers to a segment
// that is in the topology-geometry partition that has the same name as the road-attributes
// partition which contains the segment anchor.
val topoPartitionsByName: Map[String, TopologyGeometryPartition] = topoMetadata.map {
topoMeta =>
topoMeta.partition -> Await.result(readEngine.get(topoMeta,
TopologyGeometryPartition.parseFrom),
waitDuration)
}(collection.breakOut)
// Follow the segment anchor references to the decoded topology-geometry content to get the geometry
// for each paved and unpaved segment.
val pavedGeo =
getGeo(pavedSegmentAnchorIndices, roadAttributesPartition, topoPartitionsByName)
val unpavedGeo =
getGeo(unpavedSegmentAnchorIndices, roadAttributesPartition, topoPartitionsByName)
// Write out the decoded geometry as GeoJSON.
publishGeoJson(pavedGeo,
unpavedGeo,
writeEngine,
publishApi,
queryApi,
hereMapContentHrn,
hereMapContentVersion,
waitDuration)
}
} finally {
Await.result(CoordinatedShutdown(actorSystem).run(UnknownReason), Duration.Inf)
}
}
// Gets the segment references for a given segment anchor index in a road attributes partition.
private def getSegmentRefs(roadAttributesPartition: RoadAttributesPartition,
segmentAnchorIdx: Int): Iterable[Reference] =
roadAttributesPartition.segmentAnchor(segmentAnchorIdx).orientedSegmentRef.flatMap(_.segmentRef)
// Gets the topology partition names referenced by the given segment anchor indices.
private def getTopologyPartitionNames(
segmentAnchorIndices: Iterable[Int],
roadAttributesPartition: RoadAttributesPartition): Set[String] =
segmentAnchorIndices.flatMap { idx =>
getSegmentRefs(roadAttributesPartition, idx).map(_.partitionName)
}(collection.breakOut)
// Follow the segment anchor references to the decoded topology-geometry content to get the geometry
// for each paved and unpaved segment.
private def getGeo(segmentAnchorIndices: Iterable[Int],
roadAttributesPartition: RoadAttributesPartition,
topoPartitionsByName: Map[String, TopologyGeometryPartition])
: Map[String, Iterable[LineString]] =
segmentAnchorIndices
.flatMap { idx =>
// Follow the segment anchor reference to get the corresponding topology-geometry partition.
getSegmentRefs(roadAttributesPartition, idx).flatMap { ref =>
topoPartitionsByName(ref.partitionName).segment
// For each segment anchor reference, get the segment from topology-geometry which matches its identifier.
.filter(_.identifier == ref.identifier)
.flatMap(_.geometry)
.map(lineString => ref.partitionName -> lineString)
}
}
// Group the LineStrings under their respective topology partitions.
.groupBy(_._1)
.map(pair => pair._1 -> pair._2.map(_._2))
// Formats paved and unpaved LineStrings as GeoJSON.
private def makeGeoJsonFeature(paved: Boolean)(lineString: LineString) = {
def makeGeoCollection[T](geometries: Iterable[T], f: T => String) =
s"[${geometries.map(f).mkString(",")}]"
def makeGeoCoord(point: com.here.schema.geometry.v2.geometry.Point) =
s"[${point.longitude}, ${point.latitude}]"
def makeGeoJsonLineString(lineString: LineString) =
("type" -> "LineString") ~
("coordinates" -> parse(makeGeoCollection(lineString.point, makeGeoCoord)))
// Give paved and unpaved segments tooltips indicating paved or unpaved, and color
// them green and red, respectively.
("type" -> "Feature") ~
("properties" -> ("tooltip" -> (if (paved) "paved" else "unpaved")) ~
("width" -> 3.0) ~ ("style" -> ("color" -> (if (paved) "#02F93E" else "#FF3333")))) ~
("geometry" -> makeGeoJsonLineString(lineString))
}
// Write out the decoded geometry as GeoJSON.
private def publishGeoJson(pavedGeo: Map[String, Iterable[LineString]],
unpavedGeo: Map[String, Iterable[LineString]],
writeEngine: WriteEngine,
publishApi: PublishApi,
queryApi: QueryApi,
inputHrn: HRN,
inputVersion: Long,
waitDuration: Duration): Unit = {
val layerId = "roadsegments";
val commitPartitions = (pavedGeo.keySet ++ unpavedGeo.keySet).map { key =>
val pavedGeoJson = pavedGeo.getOrElse(key, Nil).map(makeGeoJsonFeature(paved = true))
val unpavedGeoJson = unpavedGeo.getOrElse(key, Nil).map(makeGeoJsonFeature(paved = false))
val geoJsonString =
compact(
render(
("type" -> "FeatureCollection") ~ ("features" -> (pavedGeoJson ++ unpavedGeoJson))))
val newPartition = NewPartition(
partition = key,
layer = layerId,
data = NewPartition.ByteArrayData(geoJsonString.getBytes("UTF-8"))
)
Await.result(writeEngine.put(newPartition), waitDuration)
}
// Write the HERE Map Content catalog's dependencies as indirect dependencies of
// our output catalog, and the HERE Map Content catalog itself as a direct
// dependency. This is good practice so that consumers of this catalog can
// perform dependency analysis if needed, for example, when scheduling downstream
// pipelines, and performing incremental processing.
val dependencies = Await
.result(queryApi.getVersion(inputVersion), waitDuration)
.dependencies
.map(_.copy(direct = false)) ++ Seq(VersionDependency(inputHrn, inputVersion, direct = true))
val baseVersion = Await.result(publishApi.getBaseVersion(), waitDuration)
Await.result(publishApi.publishBatch2(baseVersion,
Some(Seq(layerId)),
dependencies,
commitPartitions.iterator),
waitDuration)
}
}
/*
* Copyright (c) 2018-2023 HERE Europe B.V.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
import akka.actor.ActorSystem;
import akka.actor.CoordinatedShutdown;
import akka.japi.Pair;
import com.here.hrn.HRN;
import com.here.platform.data.client.engine.javadsl.DataEngine;
import com.here.platform.data.client.engine.javadsl.ReadEngine;
import com.here.platform.data.client.engine.javadsl.WriteEngine;
import com.here.platform.data.client.javadsl.*;
import com.here.platform.data.client.model.VersionDependency;
import com.here.platform.pipeline.PipelineContext;
import com.here.schema.geometry.v2.GeometryOuterClass.LineString;
import com.here.schema.rib.v2.Anchor;
import com.here.schema.rib.v2.Common;
import com.here.schema.rib.v2.RoadAttributes;
import com.here.schema.rib.v2.RoadAttributesPartitionOuterClass.RoadAttributesPartition;
import com.here.schema.rib.v2.TopologyGeometry;
import com.here.schema.rib.v2.TopologyGeometryPartitionOuterClass.TopologyGeometryPartition;
import com.typesafe.config.Config;
import com.typesafe.config.ConfigFactory;
import com.typesafe.config.ConfigValueFactory;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class RoadAttrWalkthruJava {
public static void main(String[] args)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {
// Initialize the Akka Actor System used by the Data Client Library.
Config config = ConfigFactory.empty();
config =
config.withValue(
"here.platform.data-client.endpoint-locator.discovery-service-env",
ConfigValueFactory.fromAnyRef("custom"));
config =
config.withValue(
"here.platform.data-client.endpoint-locator.discovery-service-url",
// Please use https://api-lookup.data.api.platform.hereolp.cn URL for China Environment
// We should define a custom URL, specific to China Environment, for a discovery service
// endpoint that allows discovering various Data Service APIs like publish, metadata,
// query, etc.
ConfigValueFactory.fromAnyRef("https://api-lookup.data.api.platform.here.com"));
ActorSystem actorSystem = ActorSystem.create("RoadAttrWalkthruJavaExampleApp", config);
try {
PipelineContext pipelineContext = new PipelineContext();
HRN hereMapContentHrn = pipelineContext.config().getInputCatalogs().get("hereMapContent");
long hereMapContentVersion =
pipelineContext.getJob().get().getInputCatalogs().get("hereMapContent").version();
// Choosing a Chatham Islands partition in New Zealand to keep things simple.
// Please use partition 23551658 in Tibet for China Environment.
// Feel free to replace this with one or more other partitions of interest.
List<String> roadAttrPartitionNames = Collections.singletonList("17302687");
HRN outputHrn = pipelineContext.config().getOutputCatalog();
// Initialize the I/O for the catalog.
QueryApi queryApi = DataClient.get(actorSystem).queryApi(hereMapContentHrn);
ReadEngine readEngine = DataEngine.get(actorSystem).readEngine(hereMapContentHrn);
WriteEngine writeEngine = DataEngine.get(actorSystem).writeEngine(outputHrn);
PublishApi publishApi = DataClient.get(actorSystem).publishApi(outputHrn);
// Retrieve the metadata for the road-attribute partition(s).
List<Partition> roadAttrMetadata =
queryApi
.getPartitionsById(
hereMapContentVersion,
"road-attributes",
roadAttrPartitionNames,
Collections.emptySet())
.toCompletableFuture()
.get(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
roadAttrMetadata.forEach(
metadata -> {
// For users using platform.here.com:
// https://here-tech.skawa.fun/documentation/data-client-library/dev_guide/client/get-data.html
// https://here-tech.skawa.fun/documentation/here-map-content/topics/road-layer.html
// For users using platform.hereolp.cn:
// https://here-tech.skawa.fun/cn/documentation/data-client-library/dev_guide/client/get-data.html
// https://repo.platform.hereolp.cn/artifactory/open-location-platform-docs/Data_Specifications/HERE_Map_Content/HERE_Map_Content_OLP_China_v2019-05_Data_Specification.pdf
// Retrieve the payload for the road-attribute partition and decode its contents.
RoadAttributesPartition roadAttributesPartition =
readEngine
.get(metadata, RoadAttributesPartition::parseFrom)
.toCompletableFuture()
.join();
// For users using platform.here.com:
// https://here-tech.skawa.fun/documentation/here-map-content/topics_api/com.here.schema.rib.v2.physicalattribute.html
// For users using platform.hereolp.cn:
// https://repo.platform.hereolp.cn/artifactory/open-location-platform-docs/Data_Specifications/HERE_Map_Content/HERE_Map_Content_OLP_China_v2019-05_Data_Specification.pdf
// Separate the physical attribute values combinations into those which have paved=true,
// and those which have paved=false.
Map<Boolean, List<RoadAttributes.PhysicalAttribute>> attrsByPaved =
roadAttributesPartition
.getPhysicalList()
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(RoadAttributes.PhysicalAttribute::getPaved));
List<RoadAttributes.PhysicalAttribute> paved = attrsByPaved.get(true);
List<RoadAttributes.PhysicalAttribute> unpaved = attrsByPaved.get(false);
// For users using platform.here.com:
// https://here-tech.skawa.fun/documentation/here-map-content/topics/anchor.html
// For users using platform.hereolp.cn:
// https://repo.platform.hereolp.cn/artifactory/open-location-platform-docs/Data_Specifications/HERE_Map_Content/HERE_Map_Content_OLP_China_v2019-05_Data_Specification.pdf
// Get the segment anchor indices for the paved and unpaved segments.
List<Integer> pavedSegmentAnchorIndices =
paved
.stream()
.flatMap(attr -> attr.getSegmentAnchorIndexList().stream())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
List<Integer> unpavedSegmentAnchorIndices =
unpaved
.stream()
.flatMap(attr -> attr.getSegmentAnchorIndexList().stream())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// Follow the segment anchor references to get the name of the partition(s)
// which contain the actual segment geometry within the topology-geometry layer.
Set<String> pavedTopologyPartitions =
getTopologyPartitionNames(roadAttributesPartition, pavedSegmentAnchorIndices);
Set<String> unpavedTopologyPartitions =
getTopologyPartitionNames(roadAttributesPartition, unpavedSegmentAnchorIndices);
// Retrieve the metadata for the referenced topology-geometry partitions.
Set<String> allTopoPartitions =
Stream.concat(pavedTopologyPartitions.stream(), unpavedTopologyPartitions.stream())
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
List<Partition> topoMetadata =
queryApi
.getPartitionsById(
hereMapContentVersion,
"topology-geometry",
new ArrayList<>(allTopoPartitions),
Collections.emptySet())
.toCompletableFuture()
.join();
// Retrieve the payloads and decode the content of the referenced topology-geometry
// partitions.
Map<String, TopologyGeometryPartition> topoPartitionsByName =
topoMetadata
.stream()
.map(
topoMeta ->
new Pair<>(
topoMeta.getPartition(),
readEngine
.get(topoMeta, TopologyGeometryPartition::parseFrom)
.toCompletableFuture()
.join()))
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Pair::first, Pair::second));
// Follow the segment anchor references to the decoded topology-geometry content to get
// the geometry
// for each paved and unpaved segment.
Map<String, List<LineString>> pavedGeo =
getGeo(topoPartitionsByName, roadAttributesPartition, pavedSegmentAnchorIndices);
Map<String, List<LineString>> unpavedGeo =
getGeo(topoPartitionsByName, roadAttributesPartition, unpavedSegmentAnchorIndices);
// Write out the decoded geometry as GeoJSON.
publishGeoJson(
pavedGeo,
unpavedGeo,
writeEngine,
publishApi,
queryApi,
hereMapContentHrn,
hereMapContentVersion);
});
} finally {
shutdownActorSystem(actorSystem);
}
}
private static void shutdownActorSystem(ActorSystem actorSystem) {
CoordinatedShutdown.get(actorSystem)
.runAll(CoordinatedShutdown.unknownReason())
.toCompletableFuture()
.join();
}
// Gets the segment references for a given segment anchor index in a road attributes partition.
private static Stream<Common.Reference> getSegmentRefs(
RoadAttributesPartition roadAttributesPartition, Integer segmentAnchorIdx) {
return roadAttributesPartition
.getSegmentAnchor(segmentAnchorIdx)
.getOrientedSegmentRefList()
.stream()
.map(Anchor.SegmentAnchor.OrientedSegmentReference::getSegmentRef);
}
// Follow the segment anchor references to get the name of the partition(s)
// which contain the actual segment geometry within the topology-geometry layer.
// We need to do this because it is not guaranteed that every segment anchor refers to a segment
// that is in the topology-geometry partition that has the same name as the road-attributes
// partition which contains the segment anchor.
private static Set<String> getTopologyPartitionNames(
RoadAttributesPartition roadAttributesPartition, List<Integer> segmentAnchorIndices) {
return segmentAnchorIndices
.stream()
.flatMap(idx -> getSegmentRefs(roadAttributesPartition, idx))
.map(Common.Reference::getPartitionName)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
}
// Follow the segment anchor references to the decoded topology-geometry content to get the
// geometry
// for each paved and unpaved segment.
private static Map<String, List<LineString>> getGeo(
Map<String, TopologyGeometryPartition> topoPartitionsByName,
RoadAttributesPartition roadAttributesPartition,
List<Integer> segmentAnchorIndices) {
return segmentAnchorIndices
.stream()
// Follow the segment anchor reference to get the corresponding topology-geometry partition.
.flatMap(idx -> getSegmentRefs(roadAttributesPartition, idx))
.flatMap(
ref ->
topoPartitionsByName
.get(ref.getPartitionName())
.getSegmentList()
.stream()
// For each segment anchor reference, get the segment from
// topology-geometry which matches its identifier.
.filter(seg -> seg.getIdentifier().equals(ref.getIdentifier()))
.map(TopologyGeometry.Segment::getGeometry)
.map(lineString -> new Pair<>(ref.getPartitionName(), lineString)))
// Group the LineStrings under their respective topology partitions.
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Pair::first))
.entrySet()
.stream()
.map(
pair ->
new Pair<>(
pair.getKey(),
pair.getValue().stream().map(Pair::second).collect(Collectors.toList())))
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Pair::first, Pair::second));
}
// Formats paved and unpaved LineStrings as GeoJSON.
private static String makeGeoJsonFeature(boolean paved, LineString lineString) {
StringJoiner coordJoiner = new StringJoiner(",", "[", "]");
List<String> pointsAsString =
lineString
.getPointList()
.stream()
.map(point -> "[" + point.getLongitude() + ", " + point.getLatitude() + "]")
.collect(Collectors.toList());
pointsAsString.forEach(coordJoiner::add);
// Give paved and unpaved segments tooltips indicating paved or unpaved, and color
// them green and red, respectively.
String tooltip = paved ? "paved" : "unpaved";
String color = paved ? "\"#02F93E\"" : "\"#FF3333\"";
return "{ \"type\": \"Feature\", \"geometry\": "
+ "{ \"type\": \"LineString\", \"coordinates\": "
+ coordJoiner.toString()
+ "}"
+ ", \"properties\": { \"tooltip\": \""
+ tooltip
+ "\""
+ ", \"width\" : 3.0"
+ ", \"style\": { \"color\": "
+ color
+ "}"
+ "} }";
}
// Write out the decoded geometry as GeoJSON.
private static void publishGeoJson(
Map<String, List<LineString>> pavedGeo,
Map<String, List<LineString>> unpavedGeo,
WriteEngine writeEngine,
PublishApi publishApi,
QueryApi queryApi,
HRN inputHrn,
Long inputVersion) {
Set<String> allGeoKeys =
Stream.concat(pavedGeo.keySet().stream(), unpavedGeo.keySet().stream())
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
String layerId = "roadsegments";
List<CommitPartition> commitPartitions =
allGeoKeys
.stream()
.map(
key -> {
List<String> pavedGeoJson =
pavedGeo
.getOrDefault(key, Collections.emptyList())
.stream()
.map(lineString -> makeGeoJsonFeature(true, lineString))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
List<String> unpavedGeoJson =
unpavedGeo
.getOrDefault(key, Collections.emptyList())
.stream()
.map(lineString -> makeGeoJsonFeature(false, lineString))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
List<String> allGeoJson =
Stream.concat(pavedGeoJson.stream(), unpavedGeoJson.stream())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
String geoJsonString =
allGeoJson
.stream()
.collect(
Collectors.joining(
",", "{ \"type\": \"FeatureCollection\", \"features\": [", "]}"));
NewPartition newPartition =
new NewPartition.Builder()
.withPartition(key)
.withLayer(layerId)
.withData(geoJsonString.getBytes())
.build();
return writeEngine.put(newPartition).toCompletableFuture().join();
})
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// Write the HERE Map Content catalog's dependencies as indirect dependencies of
// our output catalog, and the HERE Map Content catalog itself as a direct
// dependency. This is good practice so that consumers of this catalog can
// perform dependency analysis if needed, for example, when scheduling downstream
// pipelines, and performing incremental processing.
List<VersionDependency> dependencies =
queryApi
.getVersion(inputVersion)
.toCompletableFuture()
.join()
.getDependencies()
.stream()
.map(dep -> new VersionDependency(dep.hrn(), dep.version(), false))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
dependencies.add(new VersionDependency(inputHrn, inputVersion, true));
OptionalLong baseVersion = publishApi.getBaseVersion().toCompletableFuture().join();
publishApi
.publishBatch2(
baseVersion,
Optional.of(Collections.singletonList(layerId)),
dependencies,
commitPartitions.iterator())
.toCompletableFuture()
.join();
}
}Configure the application
The pipeline configuration files for the application are as follows:
-
The
pipeline-config.conffile declares an HRN for each input and output catalog required by the application. -
Replace `` with the HRN of the output catalog you created above.
pipeline.config {
output-catalog {hrn = "{{YOUR_CATALOG_HRN}}"}
input-catalogs {
//Please, use hrn:here-cn:data::olp-cn-here:here-map-content-china-2 on China Environment
hereMapContent {hrn = "hrn:here:data::olp-here:rib-2"}
}
}
In this tutorial, a public catalog is used - HERE Map Content Catalog. The catalog should be linked to your project first to be used within the project. To do this, replace {{YOUR_PROJECT_HRN}} the placeholder and execute the following command:
olp project resource link {{YOUR_PROJECT_HRN}} hrn:here-cn:data::olp-cn-here:here-map-content-china-2
If your command is successful, the CLI returns the following message:
Project resource hrn:here-cn:data::olp-cn-here:here-map-content-china-2 has been linked.
This pipeline-job.conf file declares the version for each input and output catalog required by the application.
pipeline.job.catalog-versions {
output-catalog {base-version = -1}
input-catalogs {
hereMapContent {
processing-type = "reprocess"
// Please, use "version = 0" on China Environment
version = 4
}
}
}
For more information on pipeline configuration, refer to the Pipelines Developer Guide.
Run the application
To run the application locally, execute the following command:
Scala
Java
mvn compile exec:java -Dexec.mainClass=RoadAttrWalkthruScala \
-Dpipeline-config.file=pipeline-config.conf \
-Dpipeline-job.file=pipeline-job.conf \
-Dhere.platform.data-client.request-signer.credentials.here-account.here-token-scope={{YOUR_PROJECT_HRN}}
mvn compile exec:java -Dexec.mainClass=RoadAttrWalkthruJava \
-Dpipeline-config.file=pipeline-config.conf \
-Dpipeline-job.file=pipeline-job.conf \
-Dhere.platform.data-client.request-signer.credentials.here-account.here-token-scope={{YOUR_PROJECT_HRN}}
Inspect the output
After running the application, inspect your output catalog as follows:
- Enter "17302687" into the search box of the Inspect tab of the catalog's
roadsegmentslayer - Click on the partition in the map to have it rendered as in the image below.
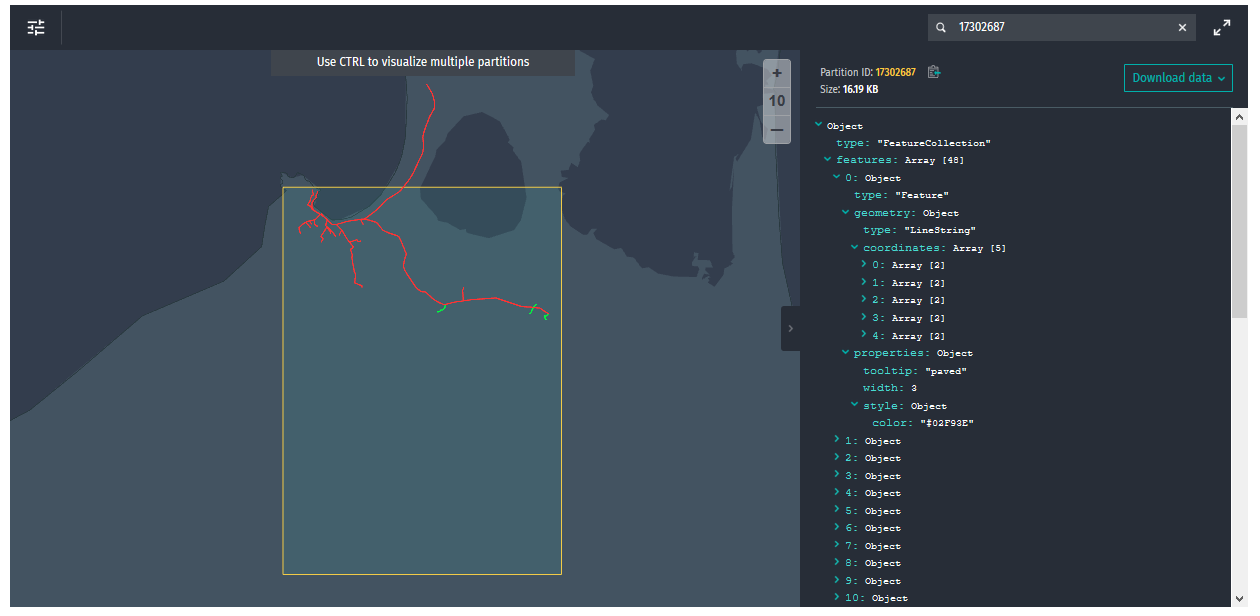
Further information
To ensure deterministic results in this tutorial, the version of the HERE Map Content input catalog is static. But you can also use getLatestVersion in the application as shown in Verify your credentials and access a catalog, remove the code extracting catalog version from the PipelineContext, and remove -Dpipeline-job.file=pipeline-job.conf from the command line to run the application locally.
You can try running this job in a pipeline. For more information on how to do this, refer to the Pipeline commands in the OLP CLI Developer Guide. Note that this standalone application can be run in batch in a pipeline, although it does not involve Spark.